Not all types of brain tumours cause symptoms, and not all cause the same. These symptoms can be caused by two main reasons:
- The tumor is pressing or encroaching on other parts of the brain and keeping them from functioning normally.
- Swelling in the brain caused directly form the tumor of for surrounding inflammation
The most common symptoms are: headache, weakness, clumsiness, difficulty in walking and seizures. Also there are non specific ones such as: vomiting, abnormalities in vision and difficulty in speech. However, non of these symptoms are brain tumour characteristic. Therefore a further diagnostic testing is needed to ensure the presence of a tumour. Usually the appearance of these symptoms is gradually and easy to be missed, even though in some cases the tumour can be suddenly manifested, for example in a stroke.
The recommended cue to seek for medical attention is when the following events are detected:
- Unexplained and persistent vomiting
- Double vision or unexplained blurring, specially on only one side
- Lethargy
- New seizures
- New pattern or type of headaches.
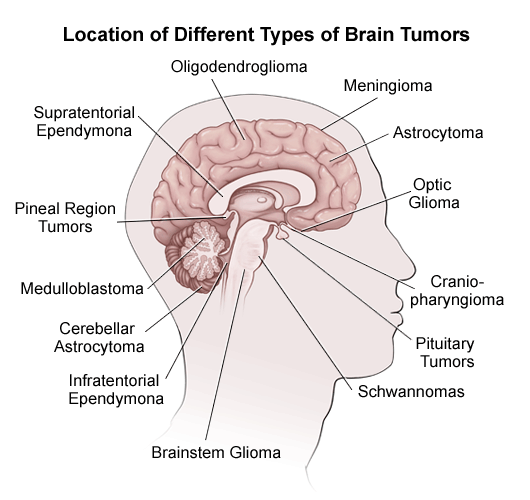
The location of the tumour is the highest determinant of the symptoms a patient experiences. There are over 120 types of brain tumours, and thus it is extremly complicated to determine the tumour type just by the symptoms the patient suffers. Moreover, the presence of the brain tumour can be due to a metastasis of a cancer originated in other part of the body.